

Explanation & Suggested Support
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Albumin -- What You Don't Know Can Kill You (Excerpts from Dr. Mercola's web site) In order to fight off invading bacteria, viruses, fungi and other invaders, your body sends the immune system into action engaging T-cells, B-cells, macrophages, eosinophils, and other immune system warriors in battle. The battle against germs is protein-based, because the immune system utilizes many protein-based substances to fight off the invasion by rapidly producing more protein-based substances to defend the body. However, there can only be a certain concentration of all proteins in the body and when the concentration of immune system proteins goes up, the concentration of other proteins must fall. Albumin is assembled in the liver from more than 500 amino acids. Portable Liver "Portable liver" because your liver is your body's chief mechanism for disarming toxins and other dangerous substances, and because albumin, which is made in your liver, does the same throughout the body. It's as if your liver has sent millions of tiny pieces of itself to every single little cell, to round up and destroy harmful substances and organisms. Albumin plays an indispensable role in maintaining the delicate chemical balance of the nourishing fluids (interstitial fluids) that surround and support the trillions of cells in your body. If these fluids are healthy, your cells will flourish. But if the fluids become polluted, or depleted of certain substances, your cells cannot help but fall ill, and disease will sweep through the body. Albumin is like a filter that removes toxins from water, like the net that scoops debris out of a swimming pool, like the dispenser that squirts extra vitamin D into milk albumin ensures that bodily fluids are clean, filled with nutrients, and properly balanced. And when you're filled with health-giving fluid, you cannot help but be healthy. |
 The most abundant protein in the bloodstream, albumin's many important duties include...
The most abundant protein in the bloodstream, albumin's many important duties include...

Lowering Albumin: the "Hidden" Problem with Infection and Disease
Medical doctors know about albumin, and often measure the amounts found in the blood with a simple blood test. Standard blood work-ups include albumin, depicting anything between 3.0 and 5.2 as "normal." Albumin has not been a focus of traditional medicine despite the fact that albumin levels are the single most important indicator of health status.
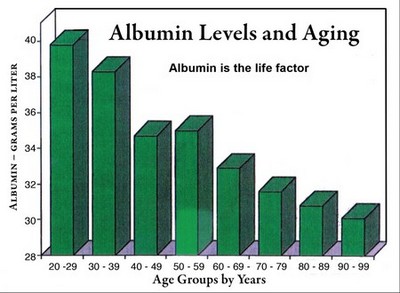
When the level of albumin in your blood drops, your risk of contracting a possibly deadly disease skyrockets. Statistical reports demonstrate that albumin levels correlate closely with age, but are not truly age-related. That is, albumin levels tend to drop as we grow older, but don't necessarily have to.
Albumin levels drop when the immune system engages in a battle with invading: Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, and other germs.
It also falls when the body is forced to deal with an onslaught of toxins and other dangerous substances that we inhale, drink, or eat, or that get into the body through the skin, respiratory system, or other ports of entry.
Temporary drops in albumin levels are necessary, and not a problem. It's as if we miss a credit card payment one month because of unexpected medical expenses, then make the missed payment, with interest, the next month. Our credit takes a small "hit," then quickly recovers.
The problem comes when we are continually battling infections and your albumin runs low for months on end -- like a person who doesn't make a credit card payment for several months, our "credit" is eventually ruined. Now we are facing serious illness, and we never seem to have enough resources to beat the disease and "get ahead."
Note from Four Winds Nutrition
Normal Albumin Levels
As albumin circulates in the blood, a simple blood test will help to determine the blood albumin status. If albumin is present within the normal range, then it indicates that the liver is functioning properly. It is a sign of liver working in good shape and as such no issues are associated with this largest organ of the body.
...in Blood
As aforementioned, albumin is one of the many constituents that circulate in the blood stream. Its presence in normal amounts in the blood, is very important for a healthy living. Blood albumin levels will be considered normal when the laboratory tests show a reading that is more than 4.0 g/dl. In general, the normal values of albumin varies between 4.0 and 5.4 g/dl. Here dl means deciliter, which is a metric unit and is equivalent to one tenth of a liter. Some laboratories regard normal albumin levels to be 3.4-5.4 (g/dl). A blood sample test that shows albumin levels to be 4.0 g/dl indicates that 1 liter of blood will contain approximately 40 grams of albumin.
...in Urine
As we all know, kidneys filter the blood to remove impurities, which are then excreted in the form of urine. Honestly speaking, urine should not contain albumin, as protein molecules are large and so easily get trapped in the kidney's filters and finally they are reabsorbed in the blood stream. However, generally albumin is found in small amounts, even when the kidneys are working in a proper manner. This generally occurs when there is too much albumin in the blood.
Many doctors regard the presence of albumin in urine as the onset of kidney dysfunction. On the whole, the normal range of urine albumin is around 0-8 mg/dl. So, if a urine sample test displays a reading of 2 mg/dl, it means 1 liter of urine contains 0.02 grams of albumin. When the amount of urine crosses this normal range, it is a symptom of kidney deterioration.
|